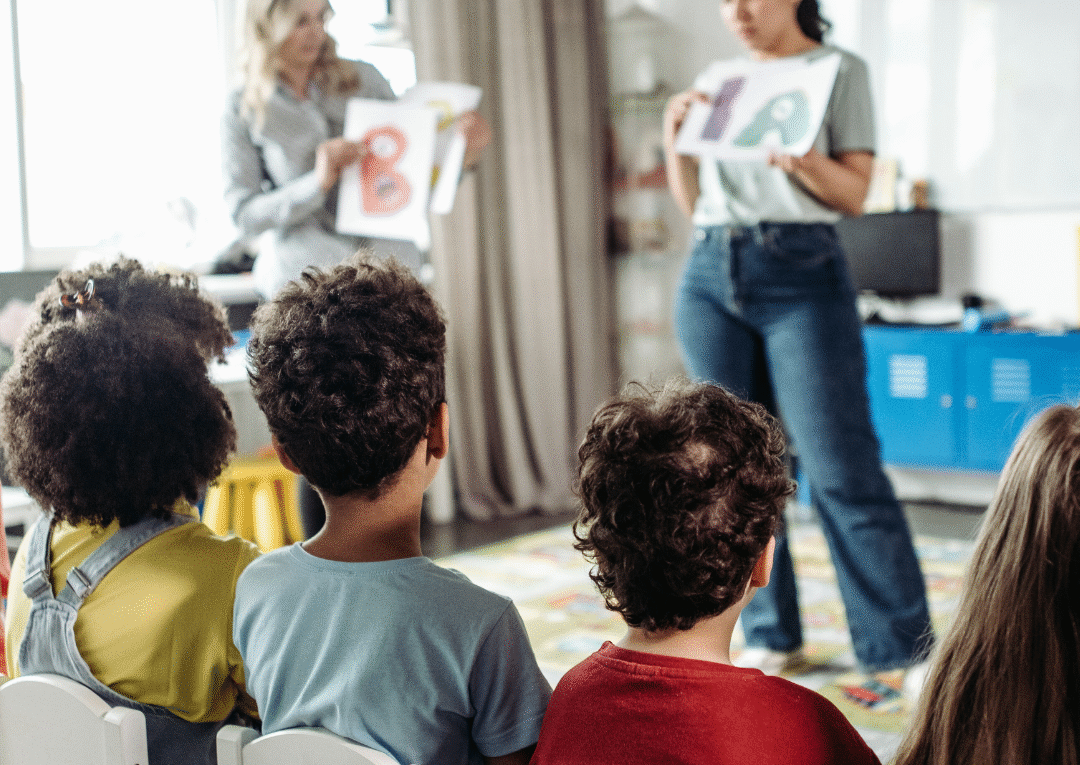
How Play Helps Kids Learn: The Essential Role of Play in Child Development
Play is a fundamental aspect of childhood that significantly contributes to a child’s learning process. Engaging in play allows children to develop critical cognitive, social, and emotional skills that enhance their overall development. As they interact with their environment, children explore concepts such as teamwork, problem-solving, and creativity, laying the groundwork for lifelong learning.
Beyond its immediate joy, play serves as a powerful educational tool. Through various forms of play—whether structured or imaginative—children learn to make decisions, take risks, and navigate challenges. These experiences foster resilience and adaptability, which are crucial in their development.
Understanding the role of play in learning is vital for parents and educators alike. By recognizing the importance of play, they can create supportive environments that encourage exploration and discovery, ultimately enhancing children’s growth and reinforcing their natural curiosity.
The Role of Play in Child Development
Play is essential for children’s growth, contributing to cognitive and physical development. Engaging in different types of play fosters problem-solving abilities, enhances language skills, and promotes motor skills needed for daily activities.
Cognitive Development Through Play
Play serves as a vital medium for cognitive development. During play, children practice problem-solving skills as they navigate challenges and obstacles. For instance, puzzle games require children to figure out how pieces fit together, promoting critical thinking.
Language development is also significantly affected. Through imaginative play, children expand their vocabulary and learn to articulate their thoughts. Interactive play with peers encourages conversation, enhancing communication skills as children share ideas and negotiate roles.
Key aspects include:
- Attention: Play activities help improve focus as children become engaged in tasks.
- Literacy skills: Storytelling and role-playing foster comprehension and narrative skills.
Physical Growth and Motor Skills
Engaging in active play is crucial for physical development. Activities like running, jumping, and climbing enhance gross motor skills, which are essential for movement stability and coordination. These skills support performance in sports and other physical activities.
Moreover, play also aids fine motor skills development. Manipulating small toys or art supplies improves hand-eye coordination and dexterity. Children learn to use tools effectively, laying the groundwork for skills such as writing.
Benefits of physical play include:
- Strength and endurance: Regular active play promotes overall fitness and health.
- Social interaction: Collaborative games foster teamwork and social skills.
Social and Emotional Advancements via Play
Play is a vital component of childhood development, fostering critical social and emotional advancements. Through various forms of play, children develop essential skills in interaction, expression, and emotional regulation.
Building Social Skills and Empathy
Dramatic play and pretend play allow children to engage in role-playing, which enhances their social skills. During these activities, they learn turn-taking and collaboration by interacting with peers in a structured setting. This interaction promotes understanding and respect for others’ viewpoints.
Children also practice conflict resolution by navigating disagreements in a playful context. This nurtures empathy, as they must consider the feelings and perspectives of peers while working towards a solution. As a result, their ability to communicate effectively and build relationships strengthens.
Fostering Self-Expression and Confidence
Play provides a platform for children to express their thoughts and emotions freely. Engaging in various activities allows them to practice self-expression, develop their unique voices. This process is crucial for building confidence.
As children explore their creativity, they experience achievements that bolster self-esteem. Role-playing different characters or scenarios encourages self-control and self-regulation, essential in managing emotions. These experiences foster resilience, equipping them to face challenges in social settings.
Creative Play and Its Impact On Learning
Creative play fosters a rich environment for children, aiding in their development through imagination and exploration. Engaging in imaginative play enables kids to express their thoughts and ideas while embarking on new experiences that fuel their interests.
Encouraging Creativity and Imagination
Creative play stimulates children’s brains, encouraging them to think outside the box. Activities like pretend play allow them to assume different roles, which enhances their storytelling skills and cognitive flexibility.
Through creative expression, children learn to make choices and solve problems. For example, building a structure with blocks requires planning and critical thinking. This hands-on experience promotes their ability to visualize concepts and translate them into physical forms.
Additionally, engaging in artistic activities such as drawing or crafting enriches their understanding of materials and techniques. These experiences not only boost self-esteem but also enhance their emotional intelligence, as they learn to communicate their feelings through art.
Exploration, Interests, and Experience
Creative play also allows children to explore their interests more deeply. When they engage in playtime activities that captivate them, it encourages curiosity and a desire to learn about related subjects.
For instance, a child who enjoys playing with toy animals may develop an interest in biology and environmental science. This engagement fosters a sense of connection between play and real-world topics, promoting lifelong learning.
Moreover, exploring new experiences through play allows them to refine motor skills and coordination. Activities like dancing, climbing, or crafting nurture their physical development while enhancing social interactions with peers in collaborative play settings.
Integrating Play in Educational Settings
Incorporating play into educational environments is essential for promoting development. By balancing screen time with hands-on activities, children can sharpen their skills in diverse areas, including language and social interaction.
Balancing Screen Time and Playtime
Many children today spend significant time in front of screens. While technology can offer educational benefits, excessive screen time can hinder developmental skills.
Strategies to Balance Playtime:
- Set Limits: Define specific timeframes for screen use, ensuring children engage in physical or imaginative play.
- Interactive Apps: Choose high-quality educational apps that encourage creativity and problem-solving.
- Scheduled Play: Incorporate scheduled breaks for play into daily routines, allowing children to explore and unwind.
Finding a balance enables children to develop crucial language skills and social interactions, fostering a well-rounded educational experience.
Play in Early Childhood Education
Play is a vital aspect of early childhood education, particularly for preschoolers. Engaging in various play activities enhances cognitive, physical, and emotional growth.
Benefits of Play for Preschoolers:
- Language Development: Play encourages communication, with children using and expanding their vocabulary through role-playing and storytelling.
- Social Skills: Cooperative games help children learn teamwork, negotiation, and empathy.
- Motor Skills: Hands-on play activities improve fine and gross motor skills, aiding in tasks such as writing and coordination.
Educators should create environments rich in opportunities for play, allowing babies and young children to experiment and learn through exploration.